Does Waxing Cause Hyperpigmentation? Unveiling the Truth
Have you ever left a salon after waxing to experience subtle changes in your skin tone after a few days? This reflects a question that sounds on the mind of every beauty enthusiast: Does waxing cause hyperpigmentation?
This question arrived after a series of continuous side effects experienced by individuals after waxing; we are here to uncover the mystery behind it. Waxing has become a popular choice for smooth, hair-free skin because of the silky and hairless finish it promises.
But behind the skin’s surface, can there be a potential side effect that lingers? Hyperpigmentation, the darkening of some skin regions, has long been a cause for cosmetic contemplation. Associating the waxing procedure to contribute to this uneven skin tone raises eyebrows and sparks curiosity.
Join us to embark on the beauty journey to discover and answer the question: Does waxing cause hyperpigmentation? Let’s delve into the intricacies of waxing and its potential ties to hyperpigmentation, separating fact from fiction in the pursuit of radiant, blemish-free skin.
Table of Contents
What is Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation is the uneven darkening of specific areas of the skin due to the overproduction of melanin (the pigment responsible for skin color, hair, and eyes). Melanin, on the other hand, is the body’s natural defense mechanism against the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
When we expose our skin to direct sunlight, the melanin in our skin fights to absorb and disperse this radiation. This forces melanocytes, a specialized cell in the epidermis, to produce more melanin cells to protect our skin further. As the production of this melanin increases, our skin pigments to a darker tone.
This darkening is what we call hyperpigmentation. However, factors such as hormonal changes, inflammation, and certain medications can trigger an abnormal increase in melanin production, leading to localized darkening or discoloration of the skin.
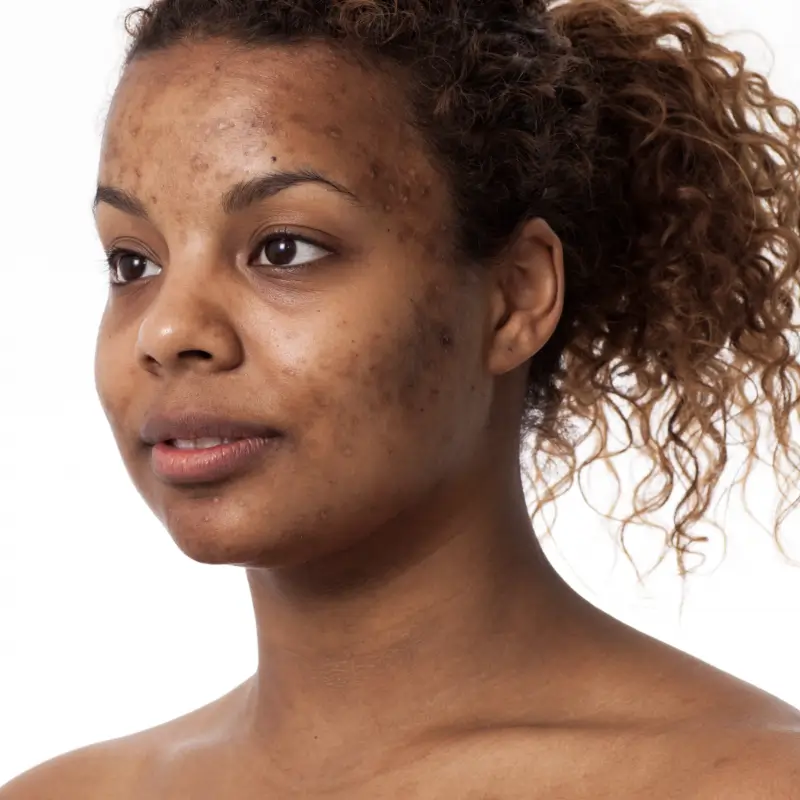

Types of hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation can be caused by various factors, each with its distinctive characteristics. These factors are what we will be classifying into types. Understanding the different kinds of hyperpigmentation is essential for effective treatment and management.
Here are some common types:
Sun-induced Hyperpigmentation
This type of hyperpigmentation is caused by overexposure or prolonged exposure of the skin to Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. This type primarily affects the face, hands, shoulders, and feet. Sun-induced hyperpigmentation is often tiny, flat, darkened patches on the sun-exposed areas.
Wearing protective clothing, minimizing sun exposure, and using sunscreen with high SPF can prevent sun-induced hyperpigmentation.
Melasma
Melasma is another type of hyperpigmentation and a prevalent skin condition. It is often associated with pregnancy, caused mainly by hormonal changes, birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy, and sun exposure.
Melasma is more common in women than men and can fade away on its own after pregnancy or after the affected woman stops taking the contraceptive pills.
This type of hyperpigmentation is larger than sun-induced hyperpigmentation, irregularly shaped brown or grayish patches, and usually on the face. It appears on the cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead.
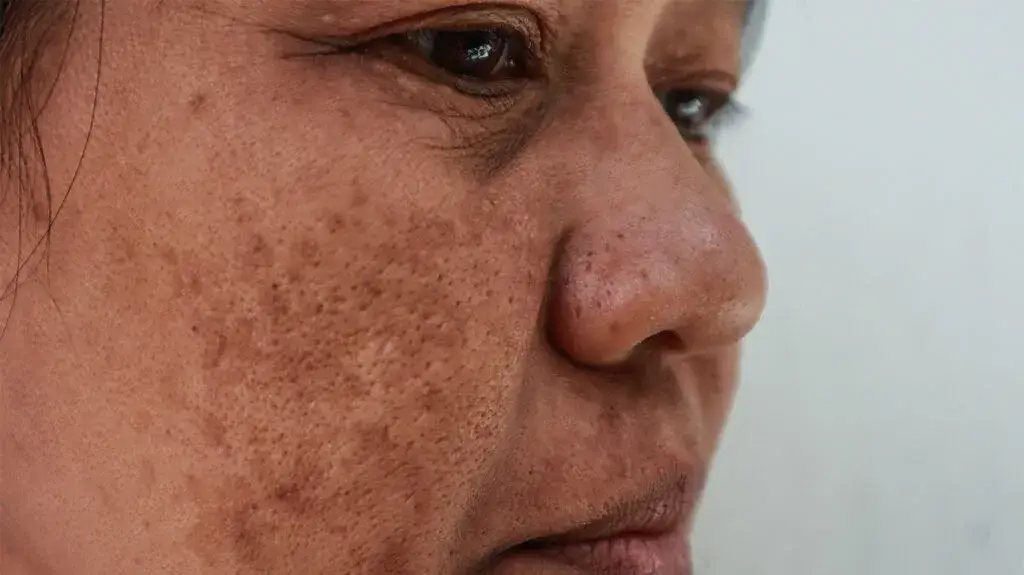

Although preventing melasma can be tricky, by sun protection, hormone regulation, and avoiding triggers can help to prevent melasma.
Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is a prevalent skin condition after the skin has been injured or inflamed. This hyperpigmentation arises in response to various skin insults, such as acne, cuts, burns, or other inflammatory skin disorders.
When your skin injury or inflammation heals, the area becomes darkened, also known as scars, and this darkening is what we call post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. PIH is a result of the consequences of skin the skin’s natural healing process and trauma on the skin.
The appearance of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation varies but typically presents as flat, darkened patches or spots in the affected areas. The color can range from pink, red, and brown to black, depending on factors and severity of the inflammation and skin tone.
PIH can fade over time in some individuals, while it might persist for extended periods in others. Often, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation can be prevented by proper wound care, acne management, and minimizing skin trauma. Topical treatments like AHAs, BHAs, and other dermatological recommended treatments and chemical peels can treat it.
Lentigines (Freckles)
Lentigines or Freckles is another common form of hyperpigmentation believed to be caused primarily by genetic predisposition and sun exposure. They are small, flat, pigmented spots that often appear on the faces of individuals with either fair or light skin. The presence of freckles is usually hereditary.
Freckles are typically round, vary in color from red and tan to brown, and are more prominent in areas exposed to sunlight, such as the face, shoulders, and arms. They may darken with sun exposure and lighten during reduced sunlight or in the winter months.
Using sunscreen and protective clothing and reducing sun exposure can help prevent freckles from darkening and limit their formation. However, it’s important to note that freckles are benign and do not pose a health risk.
What is Waxing
Waxing can be seen as a temporary hair removal procedure or method. It involves applying a wax mixture to the skin, allowing it to bond to the hair, and quickly removing the wax and unwanted hair. The wax used is made of either natural or synthetic materials.
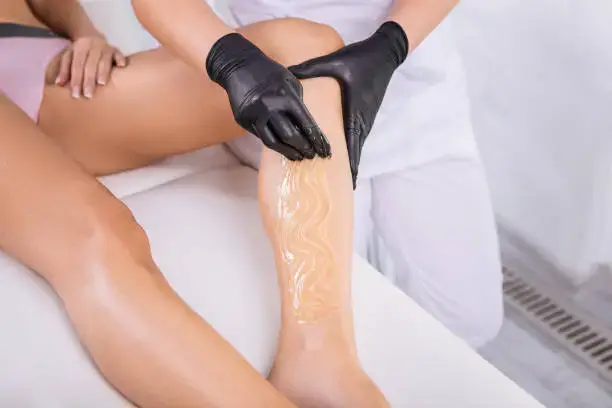

Waxing has been a popular choice in the cosmetic world for hair removal because of its smooth look and delayed ingrowing of hairs. When applied to the skin, this wax comes in a cream gel; it solidifies and encapsulates the hair follicle, uprooting the hair from its root/follicle.
The waxing procedure is employed on the following body areas: the legs, arms, armpits, face, and bikini line. The waxing process can cause temporary discomfort on the skin, but its long-lasting smooth result makes it appreciated.
Types of Waxing
There are two main waxing types, although we often see several other types. Those different types of waxing are generally grouped into hot and cold waxing. These types differ in their method of application and removal.
Hot Waxing (Hard waxing)
Hot wax is often made from natural resins like beeswax or synthetic polymers; it mostly comes in solid form and needs melting before application. This type of waxing is called hot waxing or hard waxing because of the temperature and texture of the wax, respectively.
Like the name, they harden once they cool off and are swiftly pulled to remove the unwanted hairs. Hot waxing is often advantageous for sensitive skin types; other skin types can equally use this, but specialized personnel should carry out the procedure. Hot wax is gentle on the skin and highly effective for coarse hair.
Cold Waxing (Soft Waxing)
Cold waxing, or soft waxing, is a hair removal technique that doesn’t require melting or heating. On the other hand, it is a type of waxing that comes pre-applied to strips. These waxes are often a mixture of natural resins, oils, and other ingredients. The application process is relatively easier than hot waxing.
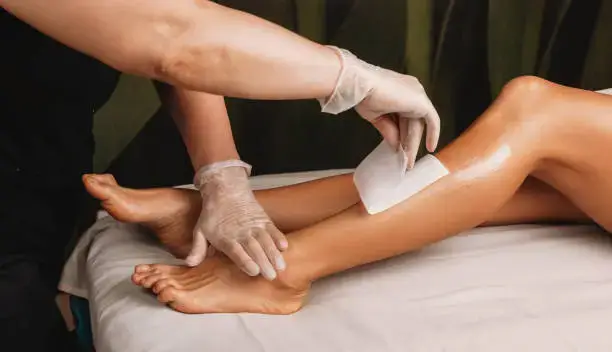
The wax strips, which adhere to both the skin and the hair, are applied and pressed on the skin. Once the strip is firmly in place, it’s swiftly pulled off against the direction of hair growth. As it lifts away, the wax takes the unwanted hair with it.
Cold waxing is a popular choice because of its convenience and easy process. It provides a temporary solution to unwanted hair removal, is swifter, and last longer than shaving. Note that this procedure may be uncomfortable.
While it might be a bit uncomfortable, many find the trade-off worthwhile for the hassle-free application and effective hair removal results.
Choosing between hot and cold waxing often depends on personal preferences, pain tolerance, and the treatment area.
Does Waxing Cause Hyperpigmentation
The relationship between waxing and hyperpigmentation has been a subject of interest in dermatological research. In this approach, a lot of findings were retrieved. The mechanical procedure of waxing, that is, the application and removal methods, causes trauma or inflammation to the skin.
This trauma is caused by the pulling of hair from the hair follicles and can trigger melanin production, thereby causing uneven darkening of the area, known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. While some dermatologists acknowledge the potential for waxing-induced hyperpigmentation, opinions may differ.
Proper waxing techniques, including using high-quality wax, ensuring adequate skin preparation, and post-waxing skincare, are recommended to minimize the risk of inflammation and subsequent hyperpigmentation.
Will Hyperpigmentation from Waxing Go Away? Find out!
Factors Influencing Skin Reaction to Waxing
Several factors influence how the skin reacts to waxing, causing hyperpigmentation. These factors include:
- Skin Sensitivity: Sensitive skin can be an underlying factor influencing skin reaction after waxing. Individuals with sensitive skin may be more prone to inflammatory responses, potentially increasing the risk of hyperpigmentation after waxing.
- Preparation and Post-care: A skin care specialist will always advise properly preparing your skin before waxing. Properly preparing the skin before waxing and following recommended aftercare practices can mitigate potential side effects, including hyperpigmentation.
- Quality of Wax: Quality is an underlining thing to look out for before undergoing waxing. The type and quality of wax used can impact the skin’s reaction. Higher-quality waxes, especially those designed for sensitive skin, may reduce the likelihood of adverse effects.
- Skin Tone: Darker skin tones may be more susceptible to hyperpigmentation because they have higher melanin production than lighter skin. Special care and attention to post-waxing care are often recommended for individuals with more melanin.
- Underlying Skin Conditions: Underlying skin conditions influence hyperpigmentation after waxing. Individuals with pre-existing skin conditions, like eczema or psoriasis, may experience heightened sensitivity and a higher risk of hyperpigmentation after waxing.
In Conclusion
The waxing process is a famous and swift hair removal method, and its relationship with hyperpigmentation remains questioned. You will achieve your quest for smooth, radiant skin waxing with insights from this post and dermatological perspectives.
Does Waxing Cause Hyperpigmentation? The impact of waxing on skin pigmentation appears to be influenced by various factors, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of the complexities involved.
Understanding hyperpigmentation involves recognizing its multifaceted origins, ranging from UV exposure to hormonal fluctuations and inflammatory responses. While not harmful in itself, hyperpigmentation can be a source of cosmetic concern for many individuals to achieve an even skin tone.
Waxing mechanical procedures can cause trauma or inflammation to the skin when not properly handled. The significance of employing proper waxing techniques, using high-quality waxes, and emphasizing individualized care based on factors like skin type, tone, and underlying conditions can help minimize the risk of waxing-induced hyperpigmentation.
We are a community of beauty enthusiasts ready to listen and provide solutions. Your experiences and insights are welcome in our comment section. Remember, your skin is your identity and requires the best treatment.
Glow right!!