What is Hyperpigmentation, A General Overview
Have you noticed dark patches or spots on your skin that won’t go away? If so, you may be experiencing a common skin condition called hyperpigmentation.
Regardless of age, gender, or skin type, hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition many people experience. The distinctive features of skin are dark patches or spots that result from an increase in melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color.
Although hyperpigmentation can occur anywhere on the body, the face, hands, and arms are the most frequently affected areas. Numerous things, such as sun exposure, hormonal changes, and inflammation, can contribute to its development.
Despite not being a serious medical condition, hyperpigmentation can cause self-consciousness and have an adverse effect on a person’s quality of life.
Individuals can better manage this condition and feel more confident in their skin by being aware of the causes and available treatments for hyperpigmentation.
At the end of this article, you will learn the following:
- What is hyperpigmentation?
- How does hyperpigmentation happen?
- If hyperpigmentation is harmful to the skin,
- How to identify hyperpigmentation on your skin when you see it
- Let’s get down to the first thing you need to know.
Table of Contents
What is hyperpigmentation?
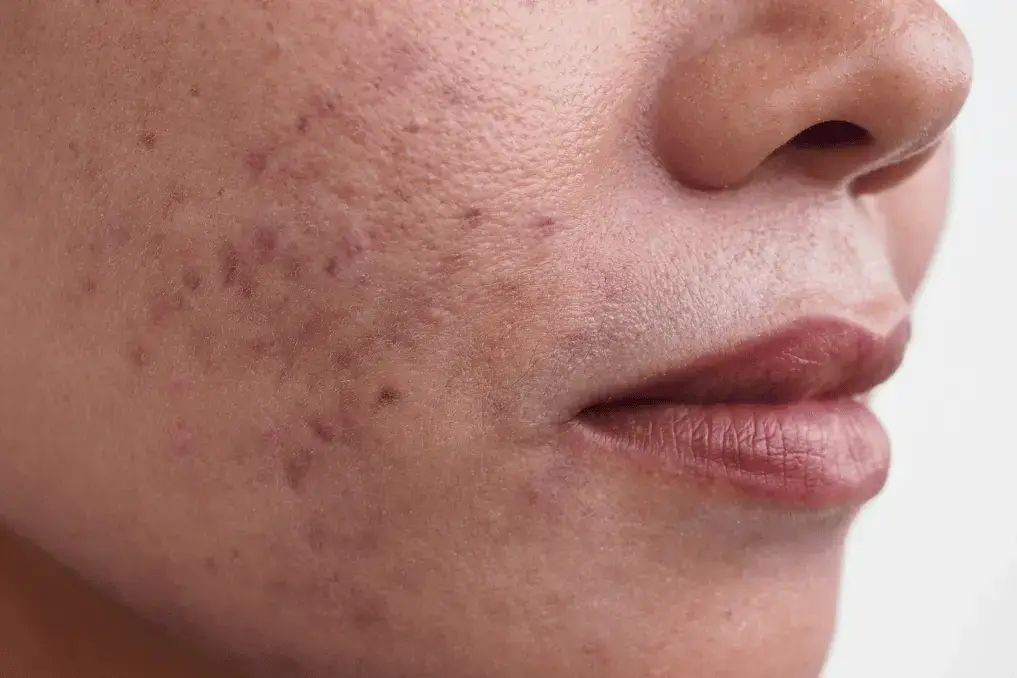
So many English and health dictionaries describe it in so many ways, but in general terms, hyperpigmentation is seen as those dark patches on the skin, or Hyperpigmentation is the darkening of a skin or nail area on by an increase in melanin production in those areas.
Melanin is a natural pigment in all living things, particularly on the skin. Melanocytes, a particular type of cell, are the ones that create the colors in melanin.
You can check out the 10 best Oil for hyperpigmentation: How they work, how to use them, risks and side effects.
How does hyperpigmentation happen?
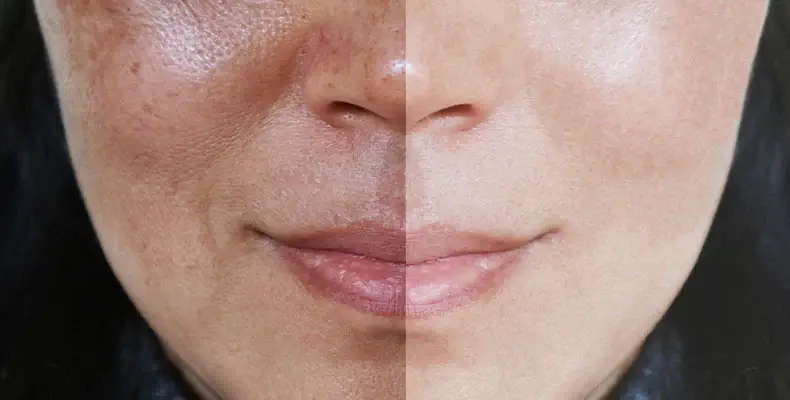
Hyperpigmentation is a long-term skin disorder wherein dead skin cells and skin oil obstruct hair follicles caused by exposure to ultraviolet rays, inflammation, drug reactions, and other skin lesions, such as acne vulgaris.
Typical signs of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, greasy skin, and scarring.
The face, upper chest, and back are among the skin areas most commonly affected by hyperpigmentation, as are other areas with a high concentration of oil glands. People with darker skin tones are likelier to develop hyperpigmentation, especially if they spend too much time in the sun.
Numerous forms of hyperpigmentation are caused by excessive synthesis of melanin. For instance, hyperpigmentation can be widespread or localized, affecting the hands’ backs and faces. An increase in melanin production is the most common cause of hyperpigmentation on the skin.
In the basal layer of the epidermis, melanocytes produce melanin. The epidermis is the topmost layer of the three that comprise the skin; the inner layers are the dermis and hypodermis.
The epidermis layer guards the body against environmental illnesses and controls how much water is lost to evaporation through the skin.
Melanocytes are neural crest-derived cells that produce melanin and are located in the bottom layer of the skin’s epidermis, the middle layer of the eye, the inner ear, the vaginal epithelium, the meninges, the bones, and the heart. The dark pigment melanin determines your skin’s color. Melanin is a pigment that gives the skin, hair, and other parts of the body their color.
As humans age, the body’s melanocyte dispersion and control management becomes less precise. When more cells are present, hyperpigmentation is caused by UV light’s promotion of melanocyte activity. Hyperpigmentation of the post-inflammatory variety is another. These skin imperfections are dark, discolored spots that appear after acne has cleared up.
Is hyperpigmentation harmful to the skin?
Hyperpigmentation is a harmless disorder that can happen to any gender of any age. However, hyperpigmentation is not a serious medical condition but can affect a person’s quality of life and loss of self-confidence.
Epidermal melasma, also seen as hyperpigmentation, can be successfully treated with oral medications such as procyanidin and vitamins A, C, and E, among other treatments.
How to identify hyperpigmentation on your skin
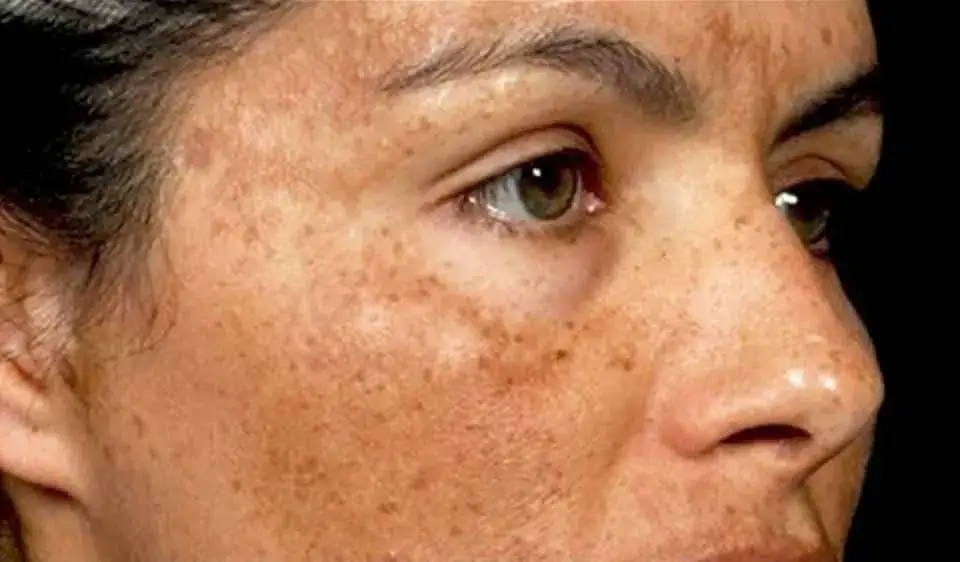
It is easy to identify hyperpigmentation when present on your skin. From the definition, it is the dark patches or dark areas of your skin that isn’t uniform to your skin color.
This can also occur when your skin generally darkens, forming shades of darker skin color.
Remember, this can also be the aftermath of acne, pimples, or any skin reaction.
In conclusion
Hyperpigmentation is harmless to the skin, but its appearance is not always good. This disorder has affected more people, especially those with dark skin.
As someone with dark skin, it is essential to protect your skin from sun exposure, which is the main cause of hyperpigmentation in the first place.
We have also understood that hyperpigmentation can affect anyone of any skin color. So, always shield your face, the back of your hands, and other affected areas with sun protective factor (SPF) for more radiant skin.
Glow right!